What is concentrated solar power ?
Ugo Pelay: As the name suggests, concentrated solar power concentrates the sun’s rays. Mirrors are used to reflect the rays toward a line or point, depending on the concentrator technology used. The irradiance is concentrated to heat a fluid called heat transfer fluid. This fluid then transmits the energy to a power cycle using an evaporator. The resulting steam then turns the turbines to generate electricity.
What are the benefits of concentrated solar power ?
UP: The main advantage of concentrated solar power plants is their heat storage capacity. Photovoltaic systems require batteries to store the electricity produced, whereas concentrated solar power enables the use of thermal storage systems that are much easier to implement, have fewer environmental impacts and are less expensive. Depending on the technology used at the power plant, the heat produced ranges between 400 and 1,000°C. It can be used to generate electricity, as seen above, or used directly by industries and processes that consume thermal energy such as desalination.
What is the difference between photovoltaic and concentrated solar power ?
UP: The difference between concentrated solar and photovoltaic power lies in their conversion methods of solar energy (in the form of electromagnetic waves). Photovoltaic panels use photovoltaic cells (electronic components) to directly convert solar energy into electrical energy based on a photoelectric effect. About 20% of solar energy is converted into electricity and 80% into heat. It is therefore a direct electronic electrical conversion process. Concentrated solar power, on the other hand, uses thermal energy from solar radiation. This is concentrated to produce high-temperature heat that is then used to turn turbines during the power cycle.
How do concentrated solar power plants work ?
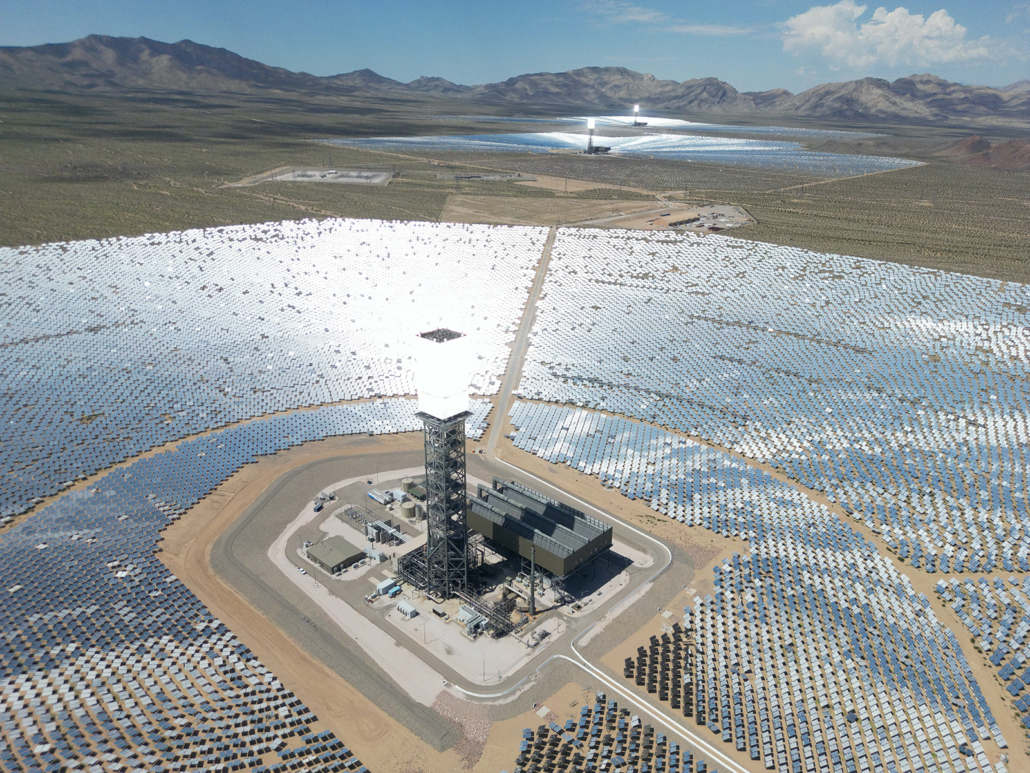
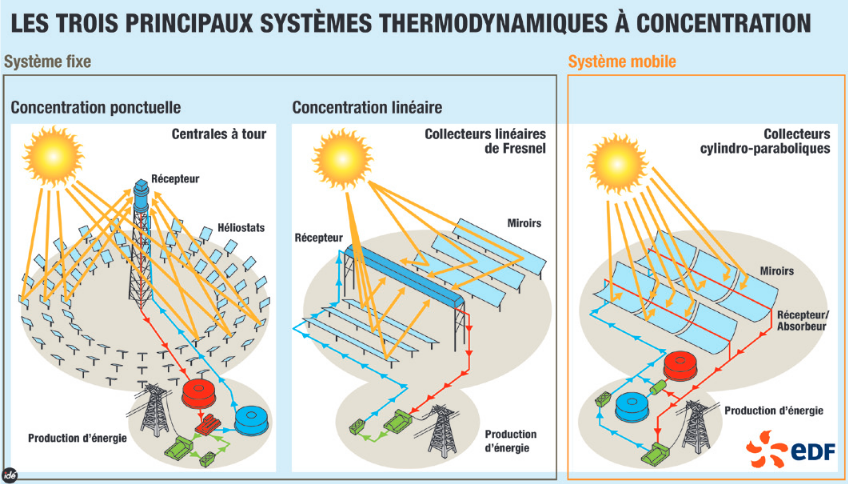
UP: Concentrated solar power mainly relies on three types of receptors or concentrators: tower, linear Fresnel, and parabolic trough.
The remote-controlled adjustable mirrors (heliostats) in the solar tower power plants reflect the sun’s rays towards a single point. The rays are concentrated in a high-efficiency cell, which is the receiver at the top of the tower. The intense concentration results in temperatures ranging between 800 and 1,000°C. The energy in the heat transfer fluid is then transferred to the power cycle (e.g. Rankine, Stirling) to produce electricity. Thermal storage systems can also be easily integrated into the plant to offset shortages or lengthen production.
Fresnel linear solar power plants use strip mirrors that can be washed automatically. They are placed in parallel rows installed close to the ground to direct the solar radiation towards stationary receiver tubes.
Parabolic trough power plants, on the other hand, have mirrors that focus the solar rays on tubes arranged at the focal axis of the concentrator. The concentrator can follow the sun’s path by rotating on an axis. Parabolic trough solar power plants can integrate thermal storage systems, just like Fresnel and tower power plants.